Page Contents
Brain Injuries Cause Problems That Many Folks Would Never Think Are Related To The Brain Injury
At Brain Injury Law of Seattle, (BILS) we have seen all manner of problems that arise from having a brain injury. There are of course the most common problems:
- Memory and recall problems
- Concentration problems
- Multitasking problems
- Dizziness and nausea
- Headaches and migraines
- Vision problems
- Light and computer screen sensitivity
- Noise sensitivity
- Sleep problems
- Hormonal problems that cause weight gain and cognitive fog
- Confusion
- Fatigue in the afternoon
- Perseveration over simple problems
How Brain Injuries Affect People?
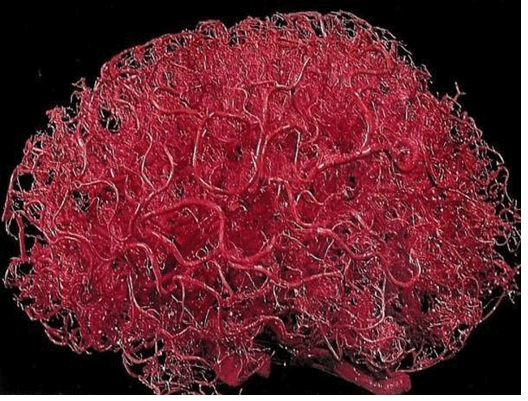
In addition to the above problems, BILS has also handled many cases where we have seen more unusual manifestations of how brain injuries affect people. When you think about it, the brain has been described as having the consistency of Jell-O or warm butter. But here’s the thing-the outer half inch or so of the brain consists of gray matter, where much of our cognition is mediated. Gray matter is not as firm as the white matter that sits beneath it though, so the differences in density can give rise to more damage at this intersection if the brain is shaken. Finally, when you add in all the blood vessels supplying the brain with oxygen and other nutrients, they serve as kind of a lattice network that contributes to the brain maintaining the Jell-O-like consistency. And there are LOTS of blood vessels and capillaries in the brain. Believe it or not, there are several hundred miles of blood vessels within the brain to ensure our brain cells get enough oxygen as shown below:
So, when the head is traumatized, it is not much different than a bowl of Jell-O with two types of Jell-O with slightly different densities-one firmer than the other, being hit and shaken up. When shaken, the intersection between the grey and white matter is the most likely to show microscopic damage that may not even show on a brain MRI.
Next, to continue with the bowl of Jell-O analogy, imagine that in this bowl of Jell-O, you had a number of fine threads spread throughout the Jell-O, rather like the image above. If shaken hard enough, the brain cells attached to the capillaries can separate from them because of the different densities, just like the grey-white matter difference. This can cause microbleeds that are also not picked up on by conventional MRI which lead to neurochemical changes that cause further cell death within the brain, in addition to the more common effects from brain injury listed above. When this cell damage occurs, there is a loss of blood flow to that area of the brain and the brain cells in that affected area effectively die off and one loses the cognitive output those cells previously provided.
Because this type of damage can occur in many parts of the brain, it can give rise to some very unusual symptoms that may not always be attributed to brain injury, but in fact, are.
Problems Brain Injuries Can Cause
By Scott Blair
Losing All Interest In Religion
At BILS, we have had several clients who, following a brain injury, went from being deeply religious to losing all interest in religion. This caused a significant amount of domestic stress because all of the remaining family members of these clients remained deeply religious and could not understand why the client had undergone such a change, especially when none of the medical providers made this connection.
BILS then looked deeply into the medical research world and found a few studies that confirmed a brain injury can result in a loss of religiosity. Neuroscientists at Northwestern University and other world-class universities have researched this issue and mapped out the brain areas that help mediate religiosity. When these areas of the brain are affected, it is therefore not surprising that the brain-injured person’s sense of belief in religion becomes affected and compromised.
However, many doctors who treat brain injuries will not do a deep dive into the medical literature because of time constraints placed upon them by their medical practices, and for this reason, may miss the connection between brain injury and more subtle effects like the loss of religiosity. It takes a careful assessment of the brain-injured person’s life to pick up on these more subtle effects.
Loss Of The Ability To Feel Happiness Or Grief
There are also other effects of a brain injury that often get missed. For example, we have handled cases where following a brain injury, had a complete loss of the ability to feel happiness or grief. This client’s medical providers noted a change in the client’s effect to a flat effect but did not explain how that occurred. Once again, a deep dive into the literature reveals that some TBI victims end up losing the ability to feel grief or happiness. In this client, she went to a close family member’s funeral and felt nothing while everyone else was expressing grief. When others around her at a wedding were all happy and full of joy, she felt nothing. It was only after bringing on a particular psychologist that this condition was deemed to be due to the brain injury but was missed by all of her treatment providers as what caused it.
Losing Interest In Sex Or Developing A Hypersexual Demeanor
Other clients have experienced a sharp change in their libido, either completely losing interest in sex or developing a hypersexual demeanor where they desired it as frequently as possible. Once again, it is the spouse of the person with the TBI who tends to feel the fallout the most in either of these scenarios. Losing one’s sex life in a marriage can be just as impactful as one partner never being satisfied, leading to tensions every bit as difficult in a marriage. These are rarer but recognized problems with brain injuries that often go overlooked because parties don’t always want to talk about their sex lives to doctors.
Brain Injury May Cause Cardiac Issues
Another serious complication that can arise from brain injuries is heart problems. Following brain injury, a “catecholamine storm” can be released in some individuals, activating the adrenal glands. Damage to the insular and hypothalamus portions of the brain as well can also lead to massive increases in catecholamines, which in turn creates “vasoconstriction” (tightening of blood vessels) and diverts oxygen to the brain that is normally utilized in cardiac tissue to promote healthy cardiac function. This can then lead to cardiogenic pulmonary edema and systemic hypertension, which in turn can lead to impaired ventricle function in the heart. This is a simplistic explanation of this process, but the potential link between brain injury and cardiac problems is well-known and must be watched for. If this is known, doctors can prescribe “beta blockers” to help control the arrhythmias from becoming harmful or dangerous to the patient.
We have observed some clients’ subsequent cardiac issues, such as arrhythmia, that may have been related to brain injury. There are specific biomarkers for cardiac problems caused by TBI, and clients who complain of new-onset cardiac issues should be referred to a cardiologist to rule out a neurogenic cause because, if ignored, they can have significant consequences if serious.
Brain Injuries Can Cause Some Serious Sleep Issues
While sleep is commonly found in TBI settings, there are some serious sleep issues that are frequently overlooked. For example, while we know that hypersomnia (not getting enough proper sleep to feel rested, hence being tired all the time) is a common diagnosis, many sleep doctors will not order a subsequent test called a multi-sleep latency test (MSLT) to determine if a rarer traumatically induced condition-narcolepsy-was the result of a brain injury.
BILS has uncovered several cases involving post-traumatic narcolepsy. Typically, these clients have a profound feeling of tiredness throughout the day despite sleeping 10-12 hours the night before. These clients are often diagnosed with simply hypersomnia or excessive tiredness without uncovering the actual underlying narcolepsy. It is essential to rule out post-traumatic narcolepsy because, if properly diagnosed, pharmaceutical interventions are available that can dramatically help a patient with this condition. However, the medications used for narcolepsy can be extremely expensive and must be factored into any future life care plan that assesses the future costs of a client’s TBI. With narcolepsy, these drug costs can stretch into the millions.
The Effects Of A TBI – The Psychiatric Changes
Another area we commonly see the effects of a TBI is in psychiatric changes that can occur following a TBI. Previously calm, kind, and soft-spoken people can become emotionally volatile and offensive in their speech and say things in public that they previously would never have said, alienating their family members and many people around them. These types of changes are often written off as psychological changes in response to musculoskeletal pain and are not always attributed to brain injury that alters the very personality of the person affected. Defendants in lawsuits are notorious for taking this approach, and BILS has learned well how best to deal with cases such as this so that such clients, despite their psychological problems, can get the help they need.
Contact Brain Injury Law Of Seattle For Legal Help If Suffered the Brain Injury
In summary, if a person who was healthy before a traumatic brain injury later starts to demonstrate an unusual physical or mental condition that nobody has tied into being caused by a brain injury, it is worth looking at this much more closely because often times there may be a medical fix for these conditions that we can help facilitate for our clients.
If you have any questions about unusual conditions, feel free to give us a call and ask us whether it may or may not be related to a recent brain injury.
Related Articles
How Long Does Road Rash Take To Heal
SYMPTOMS OF ANOXIC BRAIN INJURY HYPOXIC BRAIN INJURY
Head Injury Symptoms